How Many Types of Water Chillers Are There?
Water chillers are essential components in various industrial, commercial, and residential cooling systems. They help in removing heat from a liquid via a vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycle. The cooled liquid can then be circulated through a heat exchanger to cool air or equipment as required. These systems are commonly used in HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), manufacturing processes, data centers, medical equipment, and more.
Given the vast range of applications and technologies available, water chillers come in several types. The classification is based on various parameters such as the cooling mechanism, condenser type, heat transfer method, and application. This article delves into the major types of water chillers and provides detailed insights into their functioning, advantages, and use cases.
1. Classification Based on Cooling Mechanism
1.1 Vapor Compression Chillers
These are the most commonly used chillers in industrial and commercial applications. They operate on the vapor-compression refrigeration cycle using mechanical components.
Key Components:
1- Compressor
2- Condenser
3- Expansion valve
4- Evaporator
5- Refrigerant
Types of Compressors Used:
1- Scroll
2- Screw
3- Centrifugal
4- Reciprocating
Working Principle:
The refrigerant absorbs heat from water and evaporates in the evaporator. It is then compressed, passed through a condenser to release heat, and finally expanded before repeating the cycle.
Advantages:
1- High efficiency
2- Reliable and well-understood technology
3- Available in a wide range of capacities
Applications:
1- Office buildings
2- Manufacturing units
3- Hotels
4- Hospitals
1.2 Absorption Chillers
Absorption chillers use a heat source instead of mechanical energy to drive the refrigeration cycle. They utilize a refrigerant-absorbent pair such as water and lithium bromide.
Working Principle:
Heat from a steam, gas, or hot water source drives the refrigerant to evaporate. The vapor is then absorbed by an absorbent solution and later regenerated to continue the cycle.
Advantages:
1- Lower electricity consumption
2- Ideal for waste heat recovery
3- Environmentally friendly (uses natural refrigerants)
Applications:
1- Co-generation plants
2- Industrial processes using waste heat
3- Buildings with access to steam or solar heat
2. Classification Based on Condenser Type
2.1 Air-Cooled Chillers
Air-cooled chillers use ambient air to dissipate heat from the refrigerant via air fans and finned coils.
Key Features:
1- Do not require a cooling tower
2- Easier to install and maintain
Advantages:
1- Lower installation cost
2- Suitable for smaller or outdoor installations
Disadvantages:
1- Less energy-efficient compared to water-cooled
2- Performance affected by ambient air temperature
Applications:
1- Small to medium-sized commercial buildings
2- Remote or dry locations
2.2 Water-Cooled Chillers
These systems use water from a cooling tower to remove heat from the refrigerant. Heat is exchanged in a condenser and rejected into the atmosphere through the cooling tower.
Key Features:
1- Higher efficiency, especially in large systems
2- Requires cooling towers and additional plumbing
Advantages:
1- Better performance in high-heat environments
2- Lower operational costs in the long term
Disadvantages:
1- Higher initial investment and maintenance
2- Requires significant water usage and treatment
Applications:
1- Large commercial buildings
2- Industrial processing facilities
3- Central HVAC systems
4. Classification Based on Compressor Type
3.1 Scroll Chillers
Scroll chillers use scroll compressors, which consist of two interleaved spiral-shaped scrolls.
Advantages:
1- Compact and quiet
2- Fewer moving parts = lower maintenance
3- Good for small to medium applications
Applications:
1- Office buildings
2- Data centers
3- Retail spaces
3.2 Screw Chillers
These chillers utilize screw compressors with two helical rotors that compress the refrigerant.
Advantages:
1- High efficiency at partial loads
2- Robust and durable
3- Low vibration
Applications:
1- Process cooling
2- Medium to large-scale HVAC systems
3.3 Centrifugal Chillers
Centrifugal chillers use high-speed impellers to compress refrigerant.
Advantages:
1- Very efficient at full load
2- Suitable for high-capacity cooling
Disadvantages:
1- Expensive and complex
2- Sensitive to load fluctuations
Applications:
1- Airports
2- Hospitals
3- Large data centers
3.4 Reciprocating Chillers
These systems use piston compressors similar to internal combustion engines.
Advantages:
1- High-pressure capabilities
2- Ideal for small-scale operations
Disadvantages:
1- Noisy
2- High maintenance
Applications:
1- Laboratories
2- Small industrial setups
4. Special Purpose Chillers
Beyond conventional types, certain chillers are designed for specialized applications or environments.
4.1 Modular Chillers
Modular chillers are composed of multiple smaller chillers connected in parallel.
Advantages:
1- Scalability
2- Redundancy – if one unit fails, others can keep operating
3- Energy-efficient at partial loads
Applications:
1- Facilities with fluctuating cooling needs
2- Expandable infrastructure projects
4.2 Low-Temperature Chillers
Designed to provide chilled water at much lower temperatures than standard systems.
Applications:
1- Pharmaceuticals
2- Chemicals
3- Cold storage
4.3 Explosion-Proof Chillers
Used in hazardous environments where flammable gases or dust are present.
Applications:
1- Petrochemical plants
2- Mining
3- Military facilities
4.4 Medical and Laboratory Chillers
Highly precise chillers designed for critical and sensitive applications.
Features:
1- Accurate temperature control
2- Compact and quiet
3- Non-corrosive materials
Applications:
1- MRI machines
2- Lasers
3- Biotech labs
5. Emerging Types and Technologies
5.1 Magnetic Bearing Chillers
A new generation of chillers using magnetic levitation for compressors, eliminating mechanical contact.
Advantages:
1- No oil required
2- Lower maintenance
3- Ultra-efficient
Applications:
1- Green buildings
2- LEED-certified projects
3- High-tech campuses
5.2 Solar-Powered Absorption Chillers
Use solar thermal energy to power absorption chillers.
Advantages:
- 1- Renewable and sustainable
- 2- Excellent for sunny climates
Challenges:
- 1- High initial cost
- 2- Limited performance on cloudy days
Applications:
- 1- Eco-friendly buildings
- 2- Remote installations
6. Comparing Chiller Types
| Type | Efficiency | Initial Cost | Maintenance | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air-Cooled Chillers | Moderate | Low | Low | Small to medium buildings |
| Water-Cooled Chillers | High | High | High | Large, high-load systems |
| Absorption Chillers | Moderate (low energy use) | High | Moderate | Heat recovery & energy savings |
| Scroll Chillers | Moderate to high | Moderate | Low | Quiet, compact installations |
| Screw Chillers | High | Moderate to High | Moderate | Industrial and commercial use |
| Centrifugal Chillers | Very High | High | High | Large HVAC systems |
| Modular Chillers | High (scalable) | Medium | Moderate | Growing facilities |
| Magnetic Bearing Chillers | Very High | High | Low | Green-certified buildings |
7. Choosing the Right Water Chiller
Selecting the appropriate water chiller involves assessing several factors:
7.1 Cooling Load
Understand the amount of heat that needs to be removed. Larger systems may benefit from centrifugal or screw chillers, while smaller applications may use scroll or air-cooled chillers.
7.2 Energy Efficiency
Consider both initial costs and long-term operating costs. Magnetic bearing and absorption chillers may save energy in the long term.
7.3 Space and Location
If outdoor space is limited or installation is indoors, air-cooled chillers may be preferable. Water-cooled systems require space for cooling towers and plumbing.
7.4 Environmental Factors
Regulations on refrigerants, water usage, and energy consumption may affect chiller choice. Absorption or magnetic bearing chillers are more eco-friendly.
7.5 Budget Constraints
Initial investment varies greatly. Scroll and air-cooled chillers are budget-friendly, while centrifugal and magnetic bearing systems come with higher upfront costs.
Conclusion
Water chillers play a critical role in modern cooling systems, serving a wide array of industries and environments. From the conventional vapor-compression and absorption types to specialized and emerging technologies like magnetic bearing and solar-powered chillers, each system offers unique benefits tailored to specific needs.
Understanding the types of water chillers—based on cooling mechanisms, condenser methods, compressor types, and application-specific designs—can help facilities optimize their cooling strategy, reduce energy consumption, and ensure system reliability.
When choosing a water chiller, it’s essential to evaluate performance requirements, site conditions, energy efficiency goals, and total cost of ownership. With the continued advancement in chiller technology, more energy-efficient and eco-friendly options are becoming
How many types of water chillers does Reynold India manufacturer?
Reynold India manufactures a diverse range of water chillers tailored to various industrial applications. Their product lineup includes:
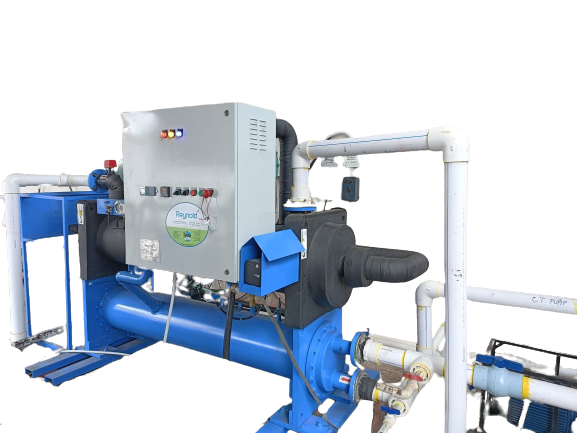
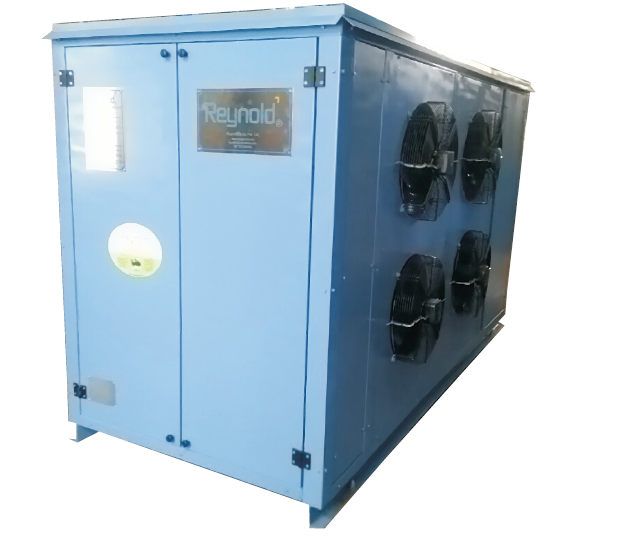




1. Screw Chillers
Air-Cooled Screw Chillers: Designed for tropical climates, these chillers are efficient and operationally reliable.
Water-Cooled Screw Chillers: These units offer high energy efficiency and are suitable for large-scale
industrial applications.
Industrial Screw Chillers: Built for heavy-duty industrial processes requiring robust cooling solutions.
2. Scroll Chillers
Air-Cooled Scroll Chillers: Compact and energy-efficient, ideal for smaller to medium-sized applications.
Water-Cooled Scroll Chillers: Provide efficient cooling with reduced noise levels, suitable for various commercial and industrial uses.
3. Reciprocating Chillers
Air-Cooled Reciprocating Chillers: Suitable for applications where space is limited and efficient cooling is required.
Water-Cooled Reciprocating Chillers: Offer higher efficiency and are ideal for larger industrial setups.
4. Customized Chillers
Reynold India also offers specialized chillers for unique applications, including:
Gas Liquefaction Chillers
Medical Equipment Chillers: Designed for cooling sensitive medical equipment like MRI and CT scan machines.
- Dual Temperature Chillers
- Milk & Beverage Chillers
- Cascade Low-Temperature Chillers
- Chillers for Hydrogen Filling Stations
- Explosion-Proof Air Conditioners for Hazardous Areas
- Methanol Chillers
- Chillers for Multi-Layer Applications
Brine Chillers: Used in processes requiring sub-zero temperatures.
5. Other Specialized Chillers
Additionally, Reynold India manufactures:
Variable Speed Chillers: Offer energy savings by adjusting compressor speed based on load.
Ammonia Chillers: Utilize ammonia as a refrigerant for industrial refrigeration needs.
Batching Plant Chillers: Designed for cooling in batching processes.
Hazardous Area Chillers: Built to operate safely in explosive or hazardous environments.
Oil Chillers: Used for cooling lubricants in machinery.
Air Chillers: Provide cooling for air-based applications.
CO₂-Based Chillers: Utilize carbon dioxide as a refrigerant, offering an environmentally friendly option.
Industrial Refrigeration Systems: Comprehensive systems for large-scale industrial cooling.
Cold Storage Solutions: Tailored for preserving perishable goods.
Vapor Recovery Units (VRU): Designed for recovering vapors in industrial processes.
This extensive range ensures that Reynold India can meet the diverse cooling requirements of various industries, from pharmaceuticals and plastics to food processing and hazardous environments.
For more detailed information on each type of chiller and their specifications, you can visit their official website: Reynold India Chillers. Sources
For more information, you can call and WhatsApp our team. Visit our website and search for Reynold India on Google. Our team will contact you as soon as possible. Customer trust is our strength. Follow Us: Facebook, Instagram, X, LinkedIn, YouTube
Click Here to Order: BUSINESS ENQUIRY FORM